Artikeldatenbank
| Autor(en) | Titel | Zeitschrift | Ausgabe | Seite | Rubrik |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kraus, Matthias; Chowdhury, Sharmistha | Sensorbasierte Identifikation der Struktursteifigkeit zur Bemessung von Stahltragwerken | Stahlbau | 2/2023 | 68-81 | Aufsätze |
KurzfassungFür die Zustandsüberwachung werden Ingenieurbauwerke zunehmend durch Monitoringsysteme ausgestattet. Besonders deutlich wird dies bei Infrastrukturbauwerken des Straßenverkehrsnetzes, da entsprechende Brücken durch die gestiegene Verkehrsstärke und Lastintensität häufig höher beansprucht werden, als das im ursprünglichen Planungsprozess berücksichtigt werden konnte. Zukünftig werden durch Sensorsysteme ausgestattete “intelligente Bauwerke” verstärkt dazu beitragen, ein besseres Verständnis zum Tragverhalten und zum Bauwerkszustand zu gewinnen. Die sachgerechte Interpretation der Monitoringdaten sowie deren Berücksichtigung bei der Bemessung von Tragwerken sind stets anspruchsvoll und mit Herausforderungen verbunden. Dieser Thematik widmet sich der vorliegende Beitrag. Es wird gezeigt, wie das Tragverhalten einer Struktur durch Sensordaten und mithilfe eines Bayesschen Ansatzes präzisiert und dies im semiprobabilistischen Sicherheitskonzept des Eurocode berücksichtigt werden kann. x | |||||
| Ungermann, Dieter; Eseme, Glen Akama | Half Monocoque Structures - Raumbildende Tragstrukturen aus Sandwichelementen | Stahlbau | 2/2023 | 82-92 | Aufsätze |
KurzfassungIm Rahmen des Forschungsprojekts “Half Monocoque Structures - Raumbildende Tragstrukturen aus Sandwichelementen” wurden theoretische und experimentelle Untersuchungen zum Tragverhalten selbsttragender Konstruktionen aus Sandwichelementen unter axialer Druckbeanspruchung durchgeführt. Ziel des Forschungsvorhabens war es, vorhandene Berechnungsansätze zur Trag- und Gebrauchstauglichkeit und die Detaillösungen zur Lasteinleitung und -verteilung zu validieren und ggf. weiterzuentwickeln. Es wurde zunächst eine selbsttragende Konstruktion aus Sandwichelementen ohne eine tragende Unterkonstruktion als Beispielobjekt entworfen. Hierzu wurden alle notwendigen Konstruktionszeichnungen und Detaillösungen zur Ausbildung der Lasteinleitungsstellen und Stoßpunkte ausgearbeitet und für diese Anwendung festgelegt. Außerdem wurde eine wirtschaftliche und ökologische Betrachtung der Bauweise anhand des Beispielobjekts vorgenommen. Die gewonnenen Erkenntnisse aus der ganzheitlichen Betrachtung der Bauweise sollen dann als Grundlage für den Erwerb einer bauaufsichtlichen Zulassung dienen. In diesem Aufsatz werden die wesentlichen Forschungsergebnisse präsentiert und die Vorzüge der Bauweise selbsttragender Konstruktionen aus Sandwichelementen ohne eine tragende Unterkonstruktion verdeutlicht. x | |||||
| 100 Jahre Versuchsanstalt für Stahl, Holz und Steine Karlsruhe | Stahlbau | 2/2023 | 92 | Empfehlungen der Redaktion | |
| Mund, Maximilian; Häßler, Dustin; Schaumann, Peter; Hothan, Sascha; Schartel, Bernhard | Experimentelle Untersuchungen zur Dauerhaftigkeit von reaktiven Brandschutzsystemen | Stahlbau | 2/2023 | 93-102 | Aufsätze |
KurzfassungReaktive Brandschutzsysteme finden im baulichen Brandschutz Anwendung zur Erhöhung des Feuerwiderstands von Stahlkonstruktionen. Neben den Anforderungen an die Feuerwiderstandsdauer können damit auch Ansprüche an die Ästhetik erfüllt werden. Die profilfolgende Applikation und die geringen Trockenschichtdicken der Produkte ermöglichen es, das filigrane Erscheinungsbild von Stahlkonstruktionen aufrechtzuerhalten. Neben der thermischen Schutzwirkung muss auch die Dauerhaftigkeit der Brandschutzbeschichtung sichergestellt werden. Die Bewertungsmethoden, die auf europäischer Ebene durch das EAD 350402-00-1106 zur Verfügung stehen, zielen auf eine Nutzungsdauer von zehn Jahren ab. Prüfverfahren für einen darüber hinausgehenden Zeitraum sind nicht beschrieben. In diesem Beitrag werden experimentelle Untersuchungen zum Einfluss der Bewitterung auf das Expansionsverhalten, zur thermischen Schutzwirkung und zu den während des Aufschäumens im Brandfall stattfindenden Reaktionen vorgestellt. Die Versuche wurden an einem wasserbasierten und einem epoxidharzbasierten reaktiven Brandschutzsystem durchgeführt. Die Ergebnisse wurden im Rahmen des IGF-Forschungsvorhabens 20470 N erzielt. x | |||||
| Calibrated design model for the compression capacity of angle members | Stahlbau | 2/2023 | 102 | Empfehlungen der Redaktion | |
| Stahlbau aktuell 2/2023 | Stahlbau | 2/2023 | 103-106 | Stahlbau aktuell | |
KurzfassungAktuelles: x | |||||
| Kongresse - Symposien - Seminare - Messen | Stahlbau | 2/2023 | 106 | Veranstaltungskalender | |
| Content: Steel Construction 2/2023 | Steel Construction | 2/2023 | Contents | ||
| Cover Picture: Steel Construction 2/2023 | Steel Construction | 2/2023 | Cover Pictures | ||
KurzfassungStub column compression test of a cold-formed C-shaped steel-section used for the validation of a new design approach which combines the AISI S100-16 Direct Strength Method with EN 1993-1-3. Failure mode of the test specimen: distortional buckling (s. paper: Ungermann, D.; Lema x | |||||
| Martins, André Dias; Camotim, Dinar; Dinis, Pedro Borges; Chen, Man-Tai; Young, Ben | Local-distortional interaction in cold-formed steel lipped channel beams: Experimental investigation - Nominee Professor Eduardo de Arantes e Oliveira Award 2021 | Steel Construction | 2/2023 | 68-77 | Articles |
KurzfassungThis paper reports an experimental investigation on the behaviour and strength of cold-formed high-strength steel (G450-G500) lipped channel beams susceptible to local-distortional interaction. The experimental campaign comprised 36 tests involving simply supported beams bent about the major axis, exhibiting various ratios between their distortional and local critical buckling moments (from 1.09 to 1.46) and acted by either uniform (20 tests) or non-uniform (trapezoidal: 16 tests) bending diagrams. The results presented and discussed consist of equilibrium paths, photos providing the evolution of the beam deformed configurations and failure moments. The paper also includes a few remarks on the design, using the Direct Strength Method, of the beams under consideration. x | |||||
| Ungermann, Dieter; Lema ski, Tim; Brune, Bettina | A Eurocode-compliant design approach for cold-formed steel sections | Steel Construction | 2/2023 | 78-92 | Articles |
KurzfassungA Eurocode-compliant design approach was developed for the design of thin-walled cold-formed steel sections which combines the AISI S100-16-Direct Strength Method (DSM) with the design provisions of EN 1993-1-3. The new design approach transfers the cross-sectional resistance determined acc. to DSM based on numerical elastic buckling analyses on the gross cross-section into the global member verification acc. to EN 1993-1-3. Additional factors were introduced to optimize the new approach, e.g., to account for the effects of the nonlinear stress distribution in cross-sections subject to local and/or distortional buckling. Within the framework of the German research project FOSTA P1328/IGF 19964, an extensive series of tests on differently shaped, perforated, and unperforated cold-formed sections in compression and bending were conducted which serve to analyze the buckling phenomena and the load-bearing capacity and to validate the new design approach. In addition, a numerical model was developed, calibrated to the tests, and used for further parametric analyses on the load-bearing capacity of cold-formed sections. x | |||||
| Nonn, Jonas; Wilden, Vera; Feldmann, Markus | A consistent approach for global buckling of steel structures | Steel Construction | 2/2023 | 93-104 | Articles |
KurzfassungThe “General Method” according to chapter 6.3.4 of EN1993-1-1 or 8.3.4 of prEN1993-1-1 deals with the verification of stability problems of frame and beam structures with loadings in-plane. The “General method” according to Eurocode is intended for the general case of a combined moment and normal force. For the choice of the reduction factor &khgr;op, there are two options for applying the reduction curve, either the minimum of lateral torsional buckling (LTB) and flexural buckling (FB) or a weighted combination of both. With the use of analytical derivations, it can be shown that this approach leads to inconsistencies which can possibly lead to incorrect results. In this paper an alternative approach is presented which leads to unification and fully mechanical justification in verification. The approach allows e.g. the verification of stability of an entire frame system directly and without interaction factors (as in the equivalent member method). In addition, the issue of a consistent equivalent imperfection is addressed. With the use of this method, geometrical non-linear analyses of structures showing out-of-plane instability can be omitted; only an in-plane calculation and a determination of a linear buckling analysis is necessary. Finally, examples are presented in this paper that demonstrate the application of the approach shown. x | |||||
| Pham, Ngoc Hieu | Investigation of sectional capacities of cold-formed perforated steel channel sections | Steel Construction | 2/2023 | 105-113 | Articles |
KurzfassungWeb holes are commonly seen in cold-formed steel channel sections to accommodate the technical services. The presence of the web holes has resulted in the reduction of the sectional capacities of the cold-formed steel sections and has been considered in the design according to the American Specification AISI S100-16 using a new approach in the design called the Direct Strength Method (DSM). This article, therefore, will use this design method to investigate the sectional capacities of perforated channel sections under compression or bending with the variation of hole sizes in relation to those of gross channel sections. Elastic buckling analysis - a compulsory requirement for application of the DSM - can be conducted using a module CUFSM software program recently developed by the American Iron and Steel Institute. The investigated channel sections are taken from the availably commercial sections. The obtained sectional capacities are seen as the opposite trends for local and distortional buckling modes, although a downtrend of the sectional capacities is found in general with the increase of hole dimensions. It was found that perforated channel sections with smaller hole height and longer hole lengths were recommended to obtain the optimum section capacities in terms of the same web hole area, but the opposite trend was seen for these sections under bending with long hole lengths. x | |||||
| Buchholz, Aljoscha; Seidel, Marc | Gap height prediction for bolted ring flange connections based on measurements | Steel Construction | 2/2023 | 114-126 | Articles |
KurzfassungWind turbine towers and their flange connections are highly fatigue loaded structures. Previous investigations have shown that initial parallel gaps between L-flange connections, which are resulting from their respective flatness of the contact surfaces, can increase fatigue loads of the connecting fasteners significantly. Flange flatness and/or gap sizes in between flanges must comply with limitations given in relevant standards and therefore must be measured after the manufacturing process and/or during installation. More than 1900 flatness measurements of several offshore wind projects were collected and used to determine initial gaps between flanges analytically. A statistical evaluation allows to determine the distribution of expected gap sizes. The increase of gap height with increasing gap length can be described with linear correlations. Furthermore, the distributions of gap heights are approximated with log-normal distributions. Parameters for generic log-normal distributions are derived considering all performed mating simulations. Following the described methodology, gaps can be determined from any large number of flatness measurements. It is proposed to consider the results for flange design. x | |||||
| Zhang, Xutong; Far, Harry; Lin, Xuqun | Deflection analysis of welded steel I-girders with corrugated webs based on first yield | Steel Construction | 2/2023 | 127-136 | Articles |
KurzfassungSinusoidal corrugated profile webs have been popularly used in steel structural designs to replace the flat webs in conventional welded beams, while there are better performances in corrugated web beams (CWBs) regarding more stability and less material used to against beam failures caused by buckling. Previous studies have provided that CWBs enabled numerous favourable benefits to be recognised as alternatives to the traditional weld beams in designing structures. Furthermore, as CWBs are proposed as the major load-carrying elements, the maximum deflection in the elastic range is one of the important beam properties that should be precisely estimated and calculated. To find an appropriate method in computing the maximum deflection of CWBs based on the first yield for civil communities in Australia, proposed equations based on other standards will be employed to calculate the theoretical results for the comparisons with simulation-based results. While applying the linear analysis simulations provided by SAP 2000, ultimate limit state design theory has also been used with requirements stated by AS 4100. In this study, the results in theoretical calculations and numerical simulations have been compared to conclude that the highly defined equations by ASTM [37] and Sause et al. [38] could precisely estimate the maximum deflections of CWBs based on the first yield in conjunction with requirements and limitations in Australian standards, which could be adequate for the structural design calculations in Australian design fields. x | |||||
| Steel Construction News 2/2023 | Steel Construction | 2/2023 | 137-138 | ECCS news | |
Kurzfassung
x | |||||
| Events: Steel Construction 2/2023 | Steel Construction | 2/2023 | 138 | Events | |
| Ernst & Sohn (Hrsg.) | UBB 2/2023 - Gesamtausgabe | UnternehmerBrief Bauwirtschaft | 2/2023 | 1-40 | Gesamtausgabe |
| Inhalt: Bauphysik 1/2023 | Bauphysik | 1/2023 | Inhalt | ||
| Titelbild: Bauphysik 1/2023 | Bauphysik | 1/2023 | Titelbild | ||
Kurzfassung
x | |||||
| Bauphysik: Jahresinhaltsverzeichnis des 44. Jahrgangs 2022 | Bauphysik | 1/2023 | 1-10 | Jahresinhaltsverzeichnis | |
| Anders, Steffen; Iravani, Ahmad; Hoffmann, Caroline; Geissler, Achim; Voss, Karsten | In-situ U-Wert-Messung - Teil 1: Vergleich von Verfahren und Einflüsse in Heizkammerversuchen | Bauphysik | 1/2023 | 1-10 | Aufsätze |
KurzfassungU-Wert-Messungen vor Ort eigenen sich für opake Bauteile unbekannter Konstruktion, bei denen eine zerstörungsfreie Aussage zu den thermischen Eigenschaften, z. B. für Sanierungsmaßnahmen erforderlich ist. In-situ U-Wert-Messungen sind Gegenstand zweier abgeschlossener Forschungsprojekte aus Deutschland und der Schweiz. Im vorliegenden Teil 1 werden die Ergebnisse des Projektes “LivingLab - Gebäudeperformance” an der Bergischen Universität Wuppertal vorgestellt. Ziel dieses Teilprojektes ist, Einflüsse auf in-situ U-Wert-Messverfahren für Mauerwerkskonstruktionen in einem Heizkammerverfahren unter kontrollierten Bedingungen herauszuarbeiten. Es kann gezeigt werden, dass bei Wärmeflussverfahren mit langer Messdauer die Größe der Platten und ihre Positionierung in Bezug auf ein Fugenraster keine messbaren Unterschiede ergeben. Bei ungedämmten Konstruktionen werden mit diesem Verfahren tendenziell geringere U-Werte, bei gedämmten Konstruktionen höhere U-Werte gemessen als bei bekanntem Materialaufbau berechnet. Vergleichend werden Kurzzeitmessungen mit der sog. “Rapid U-Value-Messtechnik (Rapid-U)” durchgeführt. Es zeigen sich größere Streuungen der Ergebnisse und höhere U-Werte als beim Wärmeflussverfahren. In Teil 2 wird ein Forschungsprojekt aus der Schweiz vorgestellt, in dessen Rahmen eine praxisorientierte Anwendungshilfe für in-situ U-Wert-Messungen erstellt wird. Als Basis dienen In-situ-Messungen mit drei unterschiedlichen Geräten und vergleichende Labormessungen. x | |||||
| Hoffmann, Caroline; Geissler, Achim; Anders, Steffen | In-situ U-Wert-Messung - Teil 2: Vergleich von Messgeräten und Anwendung vor Ort | Bauphysik | 1/2023 | 11-20 | Aufsätze |
KurzfassungU-Wert-Messungen vor Ort (in situ) eignen sich für Gebäude, bei denen die Konstruktion unbekannt ist und eine zerstörungsfreie, sichere Aussage zu den thermischen Eigenschaften getroffen werden soll. In-situ U-Wert-Messungen sind der Gegenstand von zwei kürzlich abgeschlossenen Forschungsprojekten aus Deutschland und der Schweiz. Die Grundlagen zur U-Wert-Messung, die möglichen Messverfahren, sowie Messungen mit der Wärmeflussmethode und der Rapid U-Value-Messtechnik (Rapid-U) im Labor als Bestandteil des Forschungsprojektes aus Deutschland wurden in Teil 1 dieser zweiteiligen Veröffentlichung dargestellt. Teil 2 der Veröffentlichung berichtet von einem Forschungsprojekt aus der Schweiz, in dessen Rahmen eine Anwendungshilfe für die in situ U-Wert-Messung erstellt wird. Grundlage sind U-Wert-Messungen mit am Markt erhältlichen Messgeräten, die auf eine breite Anwendung zielen. Es wurde mit zwei Messgeräten, die auf der Wärmeflussmethode basieren, und einem temperaturbasierten Messgerät gemessen. Die In-situ-Messungen werden durch vergleichende Messungen im Labor und Simulationen ergänzt. Zusätzlich werden Kontakt- und Haftmittel zur Befestigung der Sensoren an den zu messenden Bauteilen getestet. Untersucht werden schwere, homogene Bauteile, damit beziehen sich die Erkenntnisse hauptsächlich auf diesen Bauteiltyp. x | |||||
| Brandbeanspruchung von oben: bvfa-Positionspapier zur Abschottung brennbarer Rohre | Bauphysik | 1/2023 | 20 | Aktuell | |
| Rabold, Andreas; Marxt, Michaela; Schanda, Ulrich | Geeignete Beurteilungsgrößen für die Luftschalldämmung von Haustrennwänden - Bewertung der Schalldämmung bei üblichen Wohngeräuschen | Bauphysik | 1/2023 | 21-34 | Aufsätze |
KurzfassungDie Ermittlung und Bewertung der Schalldämmung eines Trennbauteils anhand einer Messgröße muss sich immer am tatsächlich erreichten Schallschutz zwischen den Wohneinheiten messen. Hieraus ergibt sich die Frage nach einer geeigneten Einzahlbewertung, die mit dem übertragenen Pegel üblicher Wohngeräusche korreliert. Soll diese Frage beantwortet werden, ist zunächst zu klären, welche Spektren übliche Wohngeräusche aufweisen. Der übertragene Pegel dieser Wohngeräusche kann anschließend anhand der Schalldämmung des Trennbauteils frequenzabhängig berechnet und gehörrichtig bewertet werden. Durch die Korrelation zwischen dem übertragenen Wohngeräuschpegel und dem Einzahlwert der Schalldämmung wird nun die Eignung der Beurteilungsgröße ersichtlich. Die beschriebene Vorgehensweise wird in der vorliegenden Veröffentlichung auf die Schalldämmung verschiedener Haustrennwände von Doppel- und Reihenhäusern angewendet, da diese bei den Mindestanforderungen nach DIN 4109-1 und den erhöhten Anforderungen nach DIN 4109-5 eine Sonderposition in Bezug auf die Anforderungshöhe einnehmen. Es werden unterschiedliche Haustrennwandtypen in Massiv- und Holzbauweise untersucht, deren Schalldämmung aus Baumessungen vorliegen. Vorschläge alternativer Bewertungsverfahren zur DIN EN ISO 717-1 und übliche Wohngeräusche konnten der Literatur entnommen und durch aktuelle Daten ergänzt werden. Neben der Eignung der Beurteilungsgrößen werden auch Zielwerte für die Schalldämmung diskutiert, die eine sichere Planung von Haustrennwänden ermöglichen sollen. x | |||||


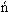 ski, T.; Brune, B., pp. 78-92). Copyright: TU Dortmund Lehrstuhl Stahlbau
ski, T.; Brune, B., pp. 78-92). Copyright: TU Dortmund Lehrstuhl Stahlbau