Journal articles
| Author(s) | Title | Journal | Issue | Page | Category |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| López-López, Andrés; Tomás, Antonio; Sánchez-Olivares, Gregorio | Behaviour of reinforced concrete rectangular sections based on tests complying with seismic construction requirements | Structural Concrete | 4/2016 | 656-667 | Technical Papers |
AbstractThe prediction of the seismic behaviour of reinforced concrete elements using numerical models has become a field of growing interest in recent years due to the importance of the effects induced by seismic loads applied to reinforced concrete structures. The simulation of the hysteretic behaviour of the plastic hinges generated in the structure when the seismic load acts requires the use of models that are able to describe the sectional behaviour of structural members. Thus, the main objective of the present paper is the adjustment of several empirical expressions that reduce the computational time needed to simulate the yield and ultimate behaviour of a given reinforced concrete rectangular section under either monotonic or cyclic loading. The expressions are calibrated with a selection of tests, taken from a published database of more than 1000 tests, according to the criterion that the selected specimens comply with the seismic construction requirements of the main international building codes (EC-2, EC-8 and ACI-318). Owing to their robustness and the acceptable computation time for low-dimensional problems, genetic algorithms are used for this calibration. The equations proposed can be employed by structural engineers for the design and analysis of actual structural elements used in ordinary reinforced concrete buildings located in seismic areas, and provide more accurate results than other expressions. x | |||||
| Chin, Siew Choo; Shafiq, Nasir; Nuruddin, Muhd Fadhil | Behaviour of RC beams with CFRP-strengthened openings | Structural Concrete | 1/2016 | 32-43 | Technical Papers |
AbstractA detailed investigation was conducted to study the behaviour of reinforced concrete (RC) beams with large openings strengthened by externally bonded carbon fibre-reinforced polymer (CFRP) laminates. A total of six simply supported beams consisting of two solid beams and four beams with openings were cast and tested under four-point bending. Each beam had a cross-section of 120 × 300 mm and length of 2000 mm. Each beam had a large opening placed symmetrically at mid-span. Test parameters included the opening shape and size as well as the strengthening configuration for the CFRP laminates. The study was conducted by way of both experimental testing and finite element analysis. The experimental results show that including a large opening at mid-span reduces the beam capacity to about 50 %. In the experimental results, strength gain due to strengthening with CFRP laminates was in the range 80-90 %. The finite element and experimental results were compared. x | |||||
| Ma, Chau-Khun; Awang, Abdullah Zawawi; Garcia, Reyes; Omar, Wahid; Pilakoutas, Kypros | Behaviour of over-reinforced high-strength concrete beams confined with post-tensioned steel straps - an experimental investigation | Structural Concrete | 5/2016 | 768-777 | Technical Papers |
AbstractThis study examines the flexural behaviour of high-strength concrete (HSC) beams confined using an innovative steel strapping tensioning technique (SSTT) able to provide active confinement. Twelve over-reinforced HSC beams (fc &equals: 50 or 80 MPa) were designed to fail prematurely by concrete crushing at mid-span. The mid-span region of eight such beams was confined externally using the SSTT with different steel strap confinement ratios, the aim of which was to delay concrete crushing. The test results are discussed in terms of the failure modes, load-deflection response and the concrete and tensile reinforcement strains observed. Although the unconfined beams failed in a brittle manner with no post-peak deflection, the steel straps were very effective at enhancing the post-peak deformation of the SSTT-confined beams by up to 126 %. Moreover, for the beams tested in this study, the use of the SSTT led to failures after yielding of the tensile reinforcement. The proposed SSTT can be used to confine HSC elements where ductility is required. x | |||||
| Ebert, Andreas; Dörre, Maik; Glienke, Ralf | Behaviour of lockbolts in slip-resistant connections for steel structures | Steel Construction | 4/2017 | 295-309 | Articles |
AbstractHV bolts are often used for safe and durable connections in steel structures. However, this well-known and established bolting system has some disadvantages. Those include the scattering of the initial preload by the torque-controlled tightening method and the risk of self-loosening during fatigue loads due to lateral displacement of the components in connections with high loads. In this respect, the lockbolt technology has some advantages regarding the initial preload and loss of preload; both will be discussed in detail in this paper. The technology was invented in the 1940s and is mainly used in automotive, aviation, truck, trailer, rail, bus, agriculture, mining and military applications. Its use in structural steelwork, and especially for slip-resistant connections, has been mainly made possible through individual experimental investigations by users of the technology. Some applications call for its use in slip-resistant connections according to EN 1090-2 and Eurocode 3, e.g. the wind industry for new tower concepts with higher hub heights, and steel girder bridges. These connections can be subjected to fatigue and/or significant load reversal. The load-bearing capacity (or slip resistance) of a slip-resistant connection is mainly determined by the level of preload in the bolt and the coating system applied to the faying surfaces. However, the preload is determined by the type of bolt, and lockbolts can be used as an alternative bolting system. This paper describes a comparative study of HV bolts and lockbolts regarding their use in slip-resistant connections for steel structures. The design and execution of lockbolts will be presented. Investigations will be presented which compare HV bolts and lockbolts regarding the assembly preload, the slip resistance by performing slip load tests and the long-term behaviour with respect to loss of preload for maintenance-free connections. Furthermore, there is a discussion of the results of an online monitoring system for measuring the preload in HV bolts and Bobtail lockbolts in an alternative tower for wind turbines with the use of slip-resistant connections. x | |||||
| Jordão, Sandra; Pinho, Marco; Martin, João Pedro; Santiago, Aldina; Neves, Luís Costa | Behaviour of laminated glass beams reinforced with pre-stressed cables | Steel Construction | 3/2014 | 204-207 | Article |
AbstractStructural glass corresponds to an innovative material with extraordinary aesthetical and architectonic potential that has undergone significant technological advances in recent years, yielding it stronger and safer. For this reason, the use of structural glass has increased considerably in the last decade and is now an unavoidable presence in most of recent reference buildings. x | |||||
| Aguiar, Eduardo Aurélio Barros; Bellucio, Ellen Kellen; El Debs, Mounir Khalil | Behaviour of grouted dowels used in precast concrete connections | Structural Concrete | 2/2012 | 84-94 | Articles |
AbstractThis research deals with the behaviour of grouted dowels used in beam-to-column connections in precast concrete structures. The research focuses primarily on the theoretical and experimental analysis of the resistance mechanism of the dowels. The experimental programme included 15 models for analysing the following variations in dowel parameters: a) dowel diameters of 16, 20 and 25 mm, b) dowel inclinations of 0° (i.e. perpendicular to the interface), 45° and 60°, c) compressive strength of classes C35 and C50 for the concrete adjacent to the dowels, and d) the absence or presence of compressive loads normal to the interface. The experimental results indicate that the ultimate capacity and shear stiffness of the inclined dowels are significantly higher than those of the perpendicular dowels. Based on these results, an analytical model is proposed that considers the influence of the parameters studied regarding the capacity of the dowel. x | |||||
| Korte, Sara; Boel, Veerle; De Corte, Wouter; De Schutter, Geert | Behaviour of fatigue loaded self-compacting concrete compared to vibrated concrete | Structural Concrete | 4/2014 | 575-589 | Technical Papers |
AbstractFatigue loading and its sometimes inevitable fatigue failure are common in many civil engineering construction projects. The behaviour of vibrated concrete (VC) under this type of loading is well understood. However, the fracture and fatigue resistance of self-compacting concrete (SCC) is poorly documented in literature. Considering the substantially different composition of the two concrete types (VC and SCC), it is uncertain whether their mechanical properties are similar or not. This paper describes the results of a series of destructive static and cyclic four-point bending tests on inverted T-shaped reinforced concrete beams, made from VC and SCC in equal quantities and of equal compressive strength. A comparison of the two concrete types is made, based on deflection, strain, crack width evolution and failure mechanism. The experiments prove that these mechanical properties of VC and SCC, subjected to a fatigue load, in some cases relate differently from a static loading process. Furthermore, the results reveal a faster concrete strain and crack width development for SCC during the fatigue tests. Regarding the number of cycles to failure, the applied load level is crucial. x | |||||
| Stanislaw Urban, Tadeusz; Goldyn, Michal Marcin | Behaviour of eccentrically loaded high-strength concrete columns intersected by lower-strength concrete slabs | Structural Concrete | 4/2015 | 480-495 | Technical Papers |
AbstractThis paper presents the results of experimental investigations of high-strength concrete edge and corner columns intersected by concrete slabs. The effect of the intersection by weaker slab concrete on the load-carrying capacities of reinforced concrete columns is investigated. The only parameter considered was the location of the column with respect to the edge of the slab. It is stated that providing a small slab overhang beyond the column edge makes it possible to increase the actual strength of the joint concrete significantly. The results of the authors' research clearly demonstrate that providing a sufficiently large slab overhang allows the designer to treat edge and corner column-slab connection joints in the same way as internal joints. Existing code provisions concerning strength of concrete in edge and corner column-slab connection joints are in some cases too conservative and require clarification. x | |||||
| Kolstein, Henk; Li, Jingbin; Koper, Axel; Gard, Wolfgang; Nijgh, Martin; Veljkovic, Milan | Behaviour of double shear connections with injection bolts | Steel Construction | 4/2017 | 287-294 | Articles |
AbstractThe RFCS project SIROCO (2014-17) included research on the further development and optimization of double shear connections with injection bolts to achieve slip- and creep-resistant bolted connections considering various influencing parameters. The type of resin, the curing condition of the resin, the geometrical and mechanical characteristics of the connection and the type of loading were studied. Results showed, for example, that of the five epoxy resins investigated, only RenGel SW404 + HY2404 (Araldite) fulfils the requirements given in Eurocode 3. A bearing stress of 175 MPa is safely allowable in the long-term without exceeding imposed deformation limits. x | |||||
| Beben, D.; Manko, Z. | Behaviour of corrugated plate culvert under backfilling loads | Steel Construction | 3/2009 | 188-202 | Articles |
AbstractThis paper is presents the results and conclusions of the field tests conducted on a backfilled shell structure made of Super Cor SC-56B corrugated steel plates in a road bridge located in Gimån, Sweden. The paper also presents the application of the FLAC (Fast Lagrangian Analysis of Continua) program, based on the finite differences method (FDM), for determining the behaviour of soil-steel bridge structures during backfilling. The assumptions of a computational 2D model of the shell structure with a non-linear “interface” layer are described. The method based on this computational model may be used with considerable success in the design calculations for this specific type of structures. The conclusions drawn from the tests can be helpful when assessing the behaviour of this type of the soil-steel bridge structure under the load of backfilling. Considering the increased application of this type of structure for small and medium-sized road and rail bridges, the conclusions drawn from the analysis conducted can be generalized to cover a whole class of such structural solutions. x | |||||
| Seo, Tae-Seok; Kim, Jung-Chul | Behaviour of concrete in a stress continuity region after cracking under restrained drying shrinkage | Structural Concrete | 2/2013 | 131-137 | Technical Papers |
AbstractSome studies have investigated the time-dependent characteristic of concrete for predicting stress under restrained shrinkage. However, these studies investigated the shrinkage behaviour of concrete in restrained conditions before cracking, and no study has yet investigated the behaviour of concrete due to restrained shrinkage in the stress continuity region after cracking. Therefore, this study investigates the shrinkage behaviour of concrete in the stress continuity region after cracking in uniaxial restrained specimens and analyses the restrained tensile stress of concrete in this region by way of a bond analysis. The results show that the effective tensile Young's modulus considering tensile creep is approx. 22-26% of the static modulus of elasticity. Moreover, the analytical results of the restrained tensile stress of concrete considering the effective tensile Young's modulus were in accordance with the experimental results. x | |||||
| Behandlung von Arbeitslohnspende bei Minijobbern | UnternehmerBrief Bauwirtschaft | 1/2016 | 11-12 | Berichte | |
AbstractVereinbaren ein Arbeitgeber und ein Minijobber eine Arbeitslohnspende für Flüchtlinge, stellt sich in der Praxis die Frage, wie diese Spende sozialversicherungsrechtlich und steuerlich zu behandeln ist. Die Antwort kommt von der Minijobzentrale. x | |||||
| Volger, A. H. | Behandlung linearer Gleichungssyteme in der Nähe der Singularität. | Bautechnik | 8/1968 | 262-266 | |
AbstractFür lineare Gleichungssysteme und die Inversion von Matrizen wird gezeigt, wie durch Verminderung der Reihenzahl und anschliessendes schrittweises Erweitern numerisch optimale Ergebnisse vor allem in der Nähe der Singularität erreicht werden können. Die Methode kann dazu dienen, in der Nähe der Singularität möglichst allen echten Informationsgehalt nutzbar zu machen. x | |||||
| Kimmling, Mathias; Hoffmann, Sabine | Behaglichkeitsmonitoring - fl√§chendeckend und kosteng√ľnstig mit der Sensorstation CoMoS | Bauphysik | 2/2019 | 111-119 | Fachthemen |
AbstractZur Erfassung von thermischen Umgebungsparametern wurde die Behaglichkeitsmessstation CoMoS (engl. Comfort Monitoring Station) entwickelt. Ziel der Entwicklung war ein kostengünstiges System mit gleichzeitig hoher Messgenauigkeit zum flächendeckenden Einsatz in Gebäuden. Diese Vorgabe wurde durch einen Aufbau erzielt, der auf kompakten, integrierten Sensoren für Lufttemperatur, relative Luftfeuchte, mittels Schwarzkugel gemessener Globe-Temperatur und Luftgeschwindigkeit basiert. x | |||||
| Dworok, Philipp-Martin; Mehra, Schew-Ram | Behaglichkeit - Wechselwirkungen bauphysikalischer Einfl√ľsse | Bauphysik | 1/2018 | 9-18 | Fachthemen |
AbstractAufgrund der stringenteren bauphysikalischen Anforderungen an Gebäude gewinnt die Behaglichkeit immer mehr an Bedeutung. Dieser Beitrag zeigt anhand einer Literaturauswertung und eigener Untersuchungsergebnisse den Stand des Wissens bezüglich der Behaglichkeit auf. Insbesondere wird dabei die Wechselwirkung thermischer und akustischer Parameter auf die Behaglichkeit herausgearbeitet. Trotz der uneinheitlichen Untersuchungsrandbedingungen, die teilweise zu widersprüchlichen Ergebnissen führen, ist festzuhalten, dass thermische und akustische Raumparameter einen interagierenden Einfluss auf die Beurteilung der Gesamtbehaglichkeit haben. Deshalb muss jeder Raumparameter, der durch menschliche Wahrnehmung erfasst und subjektiv bewertet wird, bei der Behaglichkeitsbeurteilung in Abhängigkeit der Nutzungsfunktion und Raumsituation berücksichtigt werden. Ganzheitliche Ansätze werden bereits thematisiert sowie diskutiert und sind aufgrund der aufgezeigten Wechselwirkungen zukünftig differenzierter zu betrachten, um die Behaglichkeit trotz der komplexen bauphysikalischen Einflüsse umfassend bewerten zu können. x | |||||
| Teimourtash, Shabnam | Behagliches Raumklima - Wohnen in halboffenen Räumen in ariden Regionen | Bauphysik | 4/2016 | 231-240 | Fachthemen |
AbstractDie traditionellen Stadtgebiete der ariden Regionen sind von Innenhöfen geprägt. Sie vermitteln den Eindruck, aus introvertierten Einheiten gebaut zu sein. Das Wohnen in Hofhäusern steht jedoch in enger Verbindung mit dem Außenbereich. Trotz der klimatischen Belastungen gehören offene und halboffene Räume zu den Hauptwohnräumen, wobei die Innenhöfe den Außenbereich dafür bilden. Einer der am weitesten verbreiteten halboffenen Räume der traditionellen Architektur ist der Iwan ( x | |||||
| Engel, Thomas; Noder, Julia | Begr√ľnte Fassaden aus brandschutztechnischer Sicht | Bautechnik | 8/2020 | 549-557 | Aufs√§tze |
AbstractIn den letzten Jahren gewinnen begrünte Fassaden mit Blick auf eine nachhaltige Stadtentwicklung zunehmend an Bedeutung. Zum Brandverhalten von begrünten Fassaden und der daraus folgenden Brandweiterleitung über die Fassaden steht nur eine geringe Anzahl an Erkenntnissen zur Verfügung. Dieser Aufsatz stellt den aktuellen Stand der Forschung zur brandschutztechnischen Bewertung von begrünten Fassaden dar. Darüber hinaus beschreibt er die Erkenntnisse aus vier durchgeführten orientierenden großmaßstäblichen Brandversuchen mit Fassadenbegrünungen. Bei den untersuchten Begrünungsformen handelt es sich um Kriechspindel, Blauregen, Wilden Wein, Kiwi, Stauden und Kräuter. Die Auswertung der bereits zur Verfügung stehenden und aktuell durchgeführten Versuche zeigt, dass bei der richtigen Wahl der Pflanzenart und Konstruktionsform brandschutztechnisch sichere Lösungen erzielt werden können. Im laufenden Betrieb stellt darüber hinaus die regelmäßige Pflege und Wartung eine wichtige Grundlage dar. x | |||||
| Pohl, Wolf-Hagen | Begr√ľnte Au√üenw√§nde | Bauphysik | 5/1987 | 240-251 | Fachthemen |
AbstractDer st√§dtische Raum ben√∂tigt aus verschiedenen Gr√ľnden eine Begr√ľnung. Gro√ür√§umige, erdverbundene Fl√§chen stehen nicht immer in ausreichendem Ma√üe zur Verf√ľgung, so da√ü es sinnvoll erscheint, Au√üenw√§nde als Fl√§chen f√ľr eine Begr√ľnung heranzuziehen. ln einer √úbersicht werden Pflanzen vorgestellt, die sich zum Begr√ľnen von Au√üenw√§nden eignen. Die begr√ľnte Au√üenwand soll gestalterisch/psychologische, klimatisch/hygienische, √∂kologische und bauphysikalische Funktionen erf√ľllen k√∂nnen. Der Begr√ľnung von Au√üenw√§nden werden manchmal Vorbehalte entgegengebracht, mit der Begr√ľndung, sie verursachten Sch√§den am Bauwerk. Der Erf√ľllungsgrad der verschiedenen Funktionen und die eventuell m√∂gliche Schadensverursachung werden anhand einer Literaturauswertung vorgestellt und kritisch gew√ľrdigt. x | |||||
| Jungwirth, D. | Begrenzung der Rißbreite im Stahlbeton- und Spannbetonbau aus der Sicht der Praxis (Teil 2). | Beton- und Stahlbetonbau | 8/1985 | 204-208 | Fachthemen |
| Jungwirth, D. | Begrenzung der Rißbreite im Stahlbeton- und Spannbetonbau aus der Sicht der Praxis (Teil 1). | Beton- und Stahlbetonbau | 7/1985 | 173-178 | Fachthemen |
AbstractDie Öffentlichkeit und die Rechtsprechung sehen Risse in Betonbauten als Mangel an, der die Dauerhaftigkeit in Frage stellt. Alle am Bau Beteiligten sind daher aufgefordert, aufklärend zu wirken und widerspruchsfreie, aktualisierte Regeln der Technik zur Erfüllung der Anforderung an die Gebrauchsfähigkeit und die Standsicherheit zu formulieren. Für die Dauerhaftigkeit der Bauwerke ist in erster Linie eine ausreichend dicke und dichte Betondeckung erforderlich; das wird hauptsächlich durch die Ausführungsqualität sichergestellt. Erst an zweiter Stelle kommt die kontrollierte Rißbildung, die durch die Art des Entwurfs, der technologischen Maßnahmen und durch die Wahl der Bewehrung geprägt wird. Hierzu werden Anregungen gegeben; außerdem wird ein fortschrittliches Gesamtkonzept zur Rißbegrenzung durch Bewehrung für Last- und Zwangbean- spruchung vorgeschlagen. Die bisherigen Vorschriften DIN 1045 und 4227 werden einer kritischen Beurteilung unterzogen. x | |||||
| Tue, Nguyen Viet; Turner, Katrin | Begrenzung der Rissbreite nach Eurocode 2 - Erläuterungen zum Beiwert k | Beton- und Stahlbetonbau | 8/2016 | 515-520 | Fachthemen |
AbstractDie Bemessung von Stahlbetonbauteilen erfolgt derzeit nach EC2. Ein wesentlicher Punkt in der Bemessung ist die Ermittlung der Mindestbewehrung gemäß den Angaben im Abschnitt 7.3.2. Durch die kompakte Darstellung der Gleichungen (7.1) und (7.2) in der Norm sind die mechanischen Zusammenhänge für die Anwender nicht einfach zu erkennen. Dies führt nicht selten zur falschen Interpretation der einzelnen Parameter und somit zu falschen Bemessungsergebnissen. Da die Mindestbewehrung in einzelnen Fällen die maßgebende Bewehrung für die Auslegung der Bauteile ist, insbesondere bei dicken Bauteilen, werden in diesem Beitrag die mechanischen Hintergründe für die beiden Gleichungen (7.1) und (7.2) dargestellt und erläutert. Hiermit sollte den in Ingenieurbüros tätigen Bauingenieuren mehr Sicherheit gegeben werden. x | |||||
| van Oeteren, K. A. | Begrenzung der relativen Luftfeuchtigkeit oder des Taupunktes bei der Applikation von Korrosionsschutzbeschichtungsstoffen? | Stahlbau | 9/1990 | 282 | Berichte |
| Göttlich, Peter | Begrenzung der Biegeschlankheit nach Eurocode 2 | Beton- und Stahlbetonbau | 1/2012 | 38-45 | Fachthemen |
AbstractDurchbiegungen in Stahlbetontragwerken müssen bereits im Rahmen des Entwurfes ausreichend begrenzt werden. Der Eurocode 2, der im Jahr 2012 bauaufsichtlich eingeführt wird, gibt hierzu neue Regeln vor, die im Ergebnis deutlich schärfer sind als diejenigen der DIN 1045 (Ausgabe 1988 und aktuelle Ausgabe 2008). x | |||||
| Begrenzte Verkehrssicherungspflicht auf der Baustelle | Bautechnik | 9/2001 | 672-673 | Recht | |
| Beginn einer neuen Reihe: Tragwerkplaner in der Denkmalpflege | Bautechnik | 9/2007 | 670-671 | Nachrichten | |

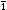 w
w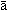 n). Der folgende Artikel befasst sich mit der Frage, wie der Iwan als klimaeffizienter Wohnraum funktioniert hat. Dafür wurden an 30 Fallbeispielen aus vier Städten der ariden Region im Iran Kriterien zur Steigerung der thermischen Behaglichkeit im Iwan untersucht, die jeweilige Position des Iwan im Grundriss analysiert und der Zusammenhang zwischen Windtürmen, Wasserbecken und Hauptwindrichtungen in den warmen Jahreszeiten und deren Einwirkung auf die Raumtemperatur im Iwan studiert.
n). Der folgende Artikel befasst sich mit der Frage, wie der Iwan als klimaeffizienter Wohnraum funktioniert hat. Dafür wurden an 30 Fallbeispielen aus vier Städten der ariden Region im Iran Kriterien zur Steigerung der thermischen Behaglichkeit im Iwan untersucht, die jeweilige Position des Iwan im Grundriss analysiert und der Zusammenhang zwischen Windtürmen, Wasserbecken und Hauptwindrichtungen in den warmen Jahreszeiten und deren Einwirkung auf die Raumtemperatur im Iwan studiert.